The Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Caring for Your Skin: Insights into Dermatology

Introduction
Dermatology, the branch of medicine dedicated to the skin, is more than just about addressing visible issues; it’s about understanding and caring for the body’s largest and most versatile organ. Our skin serves as a barrier against environmental hazards, regulates temperature, and even impacts our overall health and self-esteem. This comprehensive guide aims to enlighten you about the wonders of your skin and how to care for it, bridging the gap between everyday skincare routines and professional dermatological care.
As someone who has personally navigated the challenges of sensitive skin, I understand the importance of tailored skincare. My journey through various treatments and lifestyle changes has not only transformed my skin health but also inspired this comprehensive guide. To learn more about my story and the insights I’ve gained, check out My Skincare Journey.
Table of Contents
What You Will Learn from This Guide
This comprehensive guide to dermatology offers insights into various aspects of skin health, including:
- Understanding Your Skin: Learn about the different layers of skin and common skin types, such as normal, oily, dry, combination, and sensitive skin.
- Common Skin Conditions: Gain knowledge about conditions like acne, eczema, psoriasis, rosacea, seborrheic dermatitis, and melanoma, including their symptoms and when to consult a dermatologist.
- Dermatological Treatments and Innovations: Discover the latest advancements in skin care, including topical treatments, laser therapy, biologic therapies, and phototherapy.
- Everyday Skin Care Tips: Get practical advice on sun protection, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and conducting regular skin checks for early detection of issues.
Understanding Your Skin
The Anatomy of Skin
The Epidermis: The outermost layer, the epidermis, is the skin’s first defense against the environment. It’s composed of cells that are continuously renewed, creating a barrier against bacteria, viruses, and other potential threats.
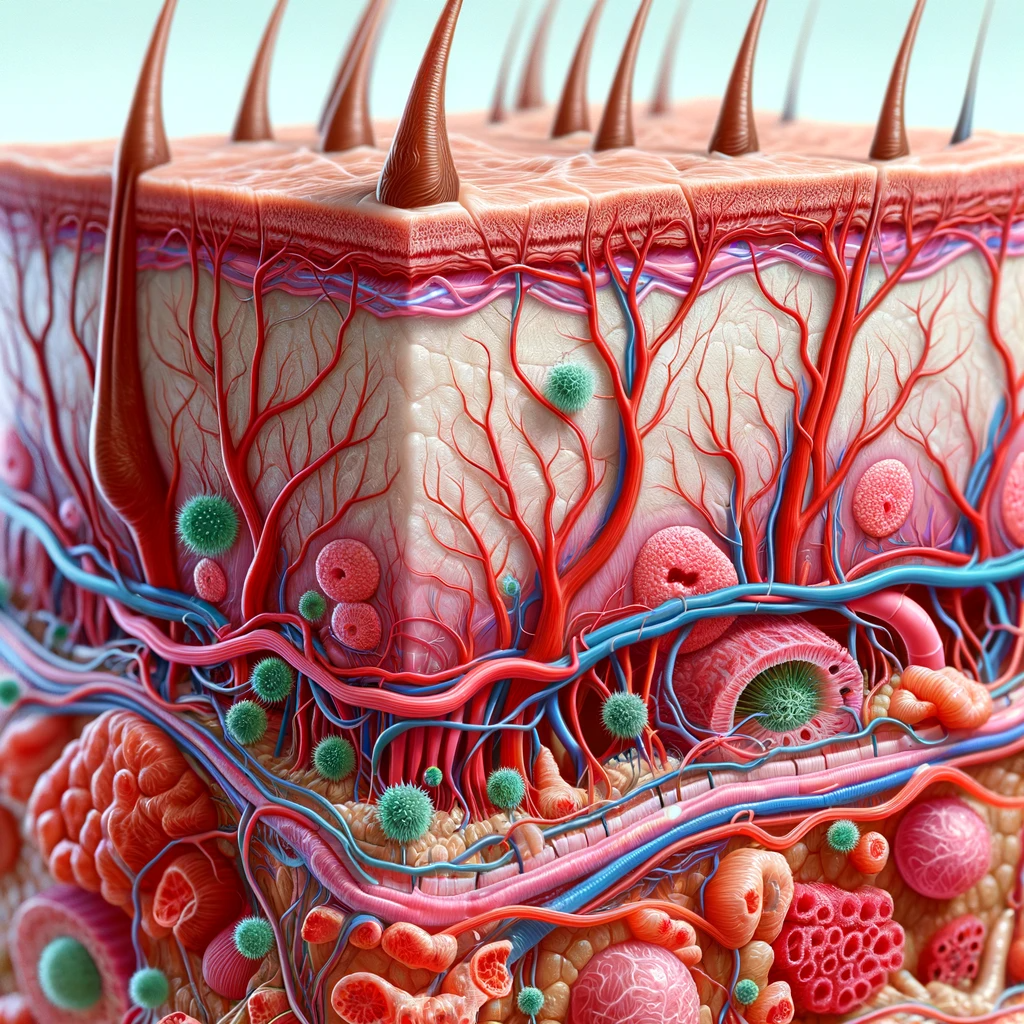
The Dermis: Beneath the epidermis lies the dermis, a thicker layer packed with blood vessels, nerve endings, sweat glands, and hair follicles. This layer is responsible for the skin’s elasticity, strength, and the ability to sense pain, heat, and cold.
The Hypodermis: The deepest layer, the hypodermis, consists of fat and connective tissue. It helps insulate the body, absorb shocks, and anchor the skin to underlying structures.
Common Skin Types
Common Skin Conditions and Their Characteristics
| Skin Condition | Symptoms | Typical Areas Affected | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| Acne | Pimples, blackheads, cysts | Face, neck, shoulders, back | Over-the-counter treatments, dermatologist consultation |
| Eczema | Dry, itchy, inflamed skin | Elbows, knees, neck, hands, face | Moisturizing creams, avoiding irritants, medical advice |
| Psoriasis | Red patches, white-silver scales | Knees, elbows, scalp, lower back | Topical treatments, phototherapy, systemic medications |
| Rosacea | Facial redness, swollen red bumps | Face, particularly cheeks and nose | Trigger management, prescription medication |
| Seborrheic Dermatitis | Red, scaly, itchy rash | Scalp, face, upper chest | Antifungal creams, medicated shampoos |
| Melanoma | Changes in moles, new growths | Any skin area | Immediate medical consultation, regular skin checks |
Understanding your skin type is crucial for effective skincare. Here are the most common skin types:
Normal Skin: Balanced in moisture and oil production, normal skin typically exhibits few blemishes and is not overly sensitive.
Oily Skin: Characterized by excess sebum production, oily skin often appears shiny, with larger pores and is prone to acne.

Dry Skin: Dry skin lacks sufficient sebum and moisture, leading to a tight, rough texture, and sometimes flaking.
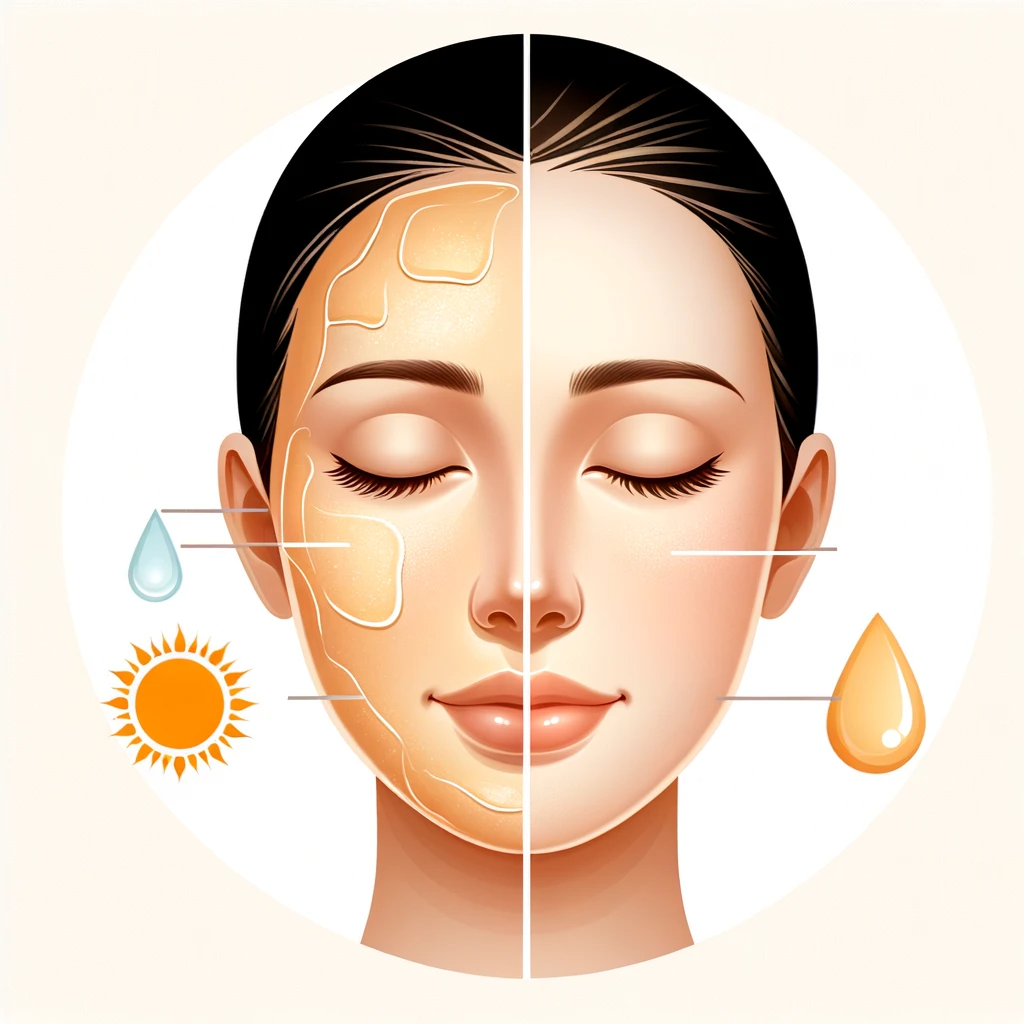
Combination Skin: This type involves having both dry and oily skin areas, typically with oiliness in the ‘T-zone’ (forehead, nose, and chin).

Understanding Your Skin
Combination Skin
Combination Skin: This skin type involves having both dry and oily skin areas. The oily areas are typically found in the ‘T-zone,’ which includes the forehead, nose, and chin, while the cheeks and other parts of the face may remain dry. Managing combination skin can be a balancing act, requiring different care strategies for different areas of the face.
Sensitive Skin
Sensitive Skin: Characterized by reactions such as redness, itching, or rashes, sensitive skin can be caused by genetic factors, environmental exposure, or underlying skin conditions. It’s essential to identify triggers and use gentle, non-irritating skincare products.
Aging Skin
Aging Skin: As we age, our skin naturally loses elasticity and moisture. Signs of aging include wrinkles, fine lines, and a decrease in the skin’s firmness and plumpness. Sun protection and products targeting hydration and collagen production can help manage aging skin.
Common Skin Conditions
Acne
Acne: One of the most common skin conditions, acne, can affect people of all ages. It’s caused by clogged hair follicles due to oil and dead skin cells, leading to pimples, blackheads, and cysts. Treatment varies depending on the severity and includes topical treatments, oral medications, and lifestyle changes.
[Insert Image: Close-up view of acne on skin, depicting various forms like pimples and blackheads.]
Eczema
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): This condition is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Eczema can be triggered by environmental factors, allergens, or stress and is often found in families with a history of allergies or asthma.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis: A chronic autoimmune condition that results in the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to scaling on the skin’s surface. These scales are typically white-silver and develop in thick, red patches, sometimes with associated pain and itching.
Rosacea
Rosacea: This condition is known for causing redness and visible blood vessels in the face. It may also produce small, red, pus-filled bumps. The causes of rosacea are not fully understood, but it can be managed with treatments and lifestyle adjustments.
Melanoma
Melanoma: The most serious type of skin cancer, melanoma forms in melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin. Early detection and treatment are crucial. Look for changes in existing moles or the appearance of new, unusual growths on the skin.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic Dermatitis: This common skin condition causes a red, scaly, itchy rash, often on the scalp. It’s not curable, but treatments can control the symptoms.

Dermatological Treatments and Innovations
Topical Treatments
Topical Treatments: Creams, gels, and ointments applied directly to the skin can effectively treat a variety of skin conditions. These include moisturizers, steroids, and medicated creams for conditions like acne and eczema.

Laser Therapy
Laser Therapy: Used for a variety of skin conditions, including removing unwanted hair, diminishing wrinkles, and treating scars and sun damage. Laser therapy can be precise and effective, with varying intensities and types.
Dermatological Treatments and Innovations (Continued)
Biologic Therapies
Biologic Therapies: These are advanced treatments, often in the form of injections, used for severe skin conditions like psoriasis. Biologics work by targeting specific parts of the immune system.
[Insert Image: Friendly Mascot explaining biologic therapies with a simple diagram of its action on the immune system.]
Phototherapy
Phototherapy: This treatment uses ultraviolet light to treat skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis. It’s a controlled exposure to UV light, administered under medical supervision.

Everyday Skin Care Tips
Sun Protection
Sun Protection: One of the most important aspects of skin care is protecting it from the sun. Use sunscreen, wear protective clothing, and avoid peak sun hours.
Healthy Lifestyle
Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, sufficient water intake, and avoiding smoking can significantly improve skin health.
Regular Skin Checks
Regular Skin Checks: Regularly checking your skin for any new moles or changes in existing moles is crucial. Early detection of skin issues can lead to better outcomes.
Conclusion
Our journey through the realm of dermatology has provided a window into the complex and fascinating world of skin care. From understanding the diverse skin types to navigating the intricacies of various skin conditions, this guide has aimed to equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your skin health. Remember, while this guide serves as a comprehensive resource, the advice of a dermatology professional is irreplaceable, especially when dealing with specific skin concerns. Stay informed, stay protected, and let your skin be a reflection of your overall well-being.
Glossary of Dermatological Terms
- Acne: A skin condition characterized by the presence of pimples, blackheads, and cysts, often caused by clogged pores.
- Biologics: Advanced medications targeting specific parts of the immune system, used in treating conditions like psoriasis.
- Dermis: The middle layer of skin containing nerves, blood vessels, and sweat glands.
- Eczema: A condition causing itchy, red, and inflamed skin, often triggered by environmental factors or allergens.
- Melanoma: A serious type of skin cancer that develops in the cells producing melanin.
- Psoriasis: A chronic autoimmune condition resulting in the rapid buildup of skin cells, leading to scaling on the skin’s surface.
- Rosacea: A skin condition causing redness and visible blood vessels in the face.
- Sebum: An oily substance produced by sebaceous glands, which helps keep the skin moisturized.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: A skin condition causing a red, scaly, itchy rash, often on the scalp.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Q: What is the best way to protect my skin from the sun?
- A: Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding the sun during peak hours are crucial steps.
- Q: Can diet impact skin health?
- A: Yes, a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can positively affect skin health.
- Q: How often should I moisturize my skin?
- A: Moisturizing should be part of your daily skincare routine, ideally after bathing and whenever your skin feels dry.
- Q: What are the signs of aging skin, and how can I address them?
- A: Signs include wrinkles, fine lines, and loss of elasticity. Using products with retinoids, peptides, and antioxidants can help mitigate these signs.
- Q: Can stress affect my skin?
- A: Absolutely. Stress can trigger or worsen conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis. Stress management techniques like meditation can be beneficial.
- Q: How do I choose the right skincare products for my skin type?
- A: Look for products formulated for your specific skin type (oily, dry, combination, or sensitive) and consider any skin concerns you may have.
- Q: What should I do if I notice a sudden change in my skin?
- A: If you observe any sudden or unusual changes, such as new growths or severe irritation, it’s important to consult a dermatologist.
- Q: Are there any general tips for maintaining healthy skin?
- A: Regular cleansing, moisturizing, sun protection, staying hydrated, and maintaining a healthy diet are key to good skin health.
