This post may contain affiliate links which means I may receive a commission for purchases made through links. As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases. I will only recommend products that I have personally used! Learn more on my Private Policy page.
Learn About Oral Treatments for Resistant Seborrheic Dermatitis
- Definition, symptoms, causes, and prevalence of seborrheic dermatitis.
- Overview of traditional treatment options and challenges in managing resistant seborrheic dermatitis.
- Review of emerging oral treatment options, their mechanisms of action, efficacy, and patient-specific considerations.
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common chronic skin condition that primarily affects areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the scalp, face, and upper trunk. It is characterized by redness, itching, and flaking of the skin, often leading to significant discomfort and self-consciousness in affected individuals. The condition can be particularly challenging to manage when it becomes resistant to conventional treatment approaches, necessitating the exploration of emerging oral treatment options.
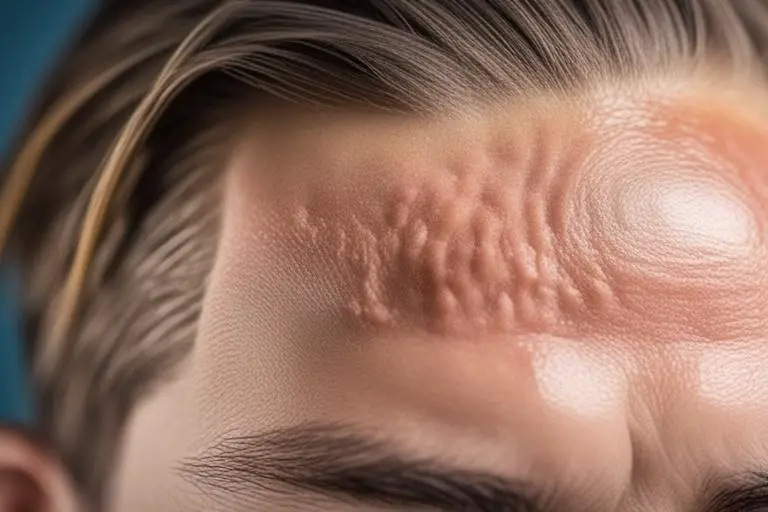
Definition and Symptoms of Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis presents as red, inflamed skin covered by greasy or dry scales, with the severity of symptoms varying from mild itching and flaking to more pronounced erythema and discomfort. The condition commonly affects the scalp, eyebrows, eyelids, nasolabial folds, ears, sternum, and intertriginous areas, contributing to its impact on quality of life.
Causes and Triggers of the Condition
The exact etiology of seborrheic dermatitis is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. The overgrowth of the yeast Malassezia species, alterations in sebum composition, and individual susceptibility are thought to contribute to disease development and exacerbation.
Prevalence and Demographics of Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis affects individuals of all ages, with a peak incidence in infancy (cradle cap) and another peak in adulthood. The condition is more prevalent in men than women and is commonly associated with other skin disorders such as rosacea and psoriasis.

Current Treatment Options for Seborrheic Dermatitis
Overview of Traditional Treatment Options
1. Medicated Shampoos
Medicated shampoos containing ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or pyrithione zinc are commonly used to reduce scaling and inflammation associated with seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp.
2. Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are employed to alleviate itching and inflammation, but long-term use is restricted due to the risk of skin atrophy and other adverse effects.
3. Antifungal Agents
Topical antifungal agents such as clotrimazole and miconazole can help manage seborrheic dermatitis by targeting the overgrowth of Malassezia.
4. Calcineurin Inhibitors
Calcineurin inhibitors like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are reserved for cases refractory to other treatments, as they carry a risk of lymphoma and skin malignancies.
Efficacy and Limitations of Existing Treatments
While traditional treatments can effectively control mild to moderate seborrheic dermatitis, their efficacy diminishes in cases of resistant or widespread disease. Furthermore, concerns regarding safety, tolerability, and long-term management warrant the exploration of alternative therapeutic strategies.
Challenges in Managing Resistant Seborrheic Dermatitis
The management of resistant seborrheic dermatitis poses a significant clinical challenge, often necessitating prolonged treatment duration, combination therapy, and the consideration of systemic agents to achieve adequate disease control.
Oral Antifungal Resistance in Seborrheic Dermatitis
Understanding Oral Antifungal Resistance
Oral antifungal resistance refers to the reduced susceptibility of Malassezia species to systemic antifungal agents, leading to treatment failure and disease persistence.
Factors Contributing to Oral Antifungal Resistance
Prolonged or repeated use of oral antifungal medications, suboptimal dosing, and patient non-compliance are factors that can contribute to the development of oral antifungal resistance.
Impact of Oral Antifungal Resistance on Seborrheic Dermatitis Treatment
The emergence of oral antifungal resistance presents a formidable obstacle in the management of seborrheic dermatitis, necessitating the evaluation of alternative oral treatment modalities.

Emerging Oral Treatments for Resistant Seborrheic Dermatitis
For individuals with resistant seborrheic dermatitis, emerging oral treatment options offer new hope. These innovations are designed to provide enhanced efficacy and improved disease control, addressing the limitations of traditional topical therapies.
Mechanisms of Action for Oral Treatments
Emerging oral treatments for seborrheic dermatitis primarily target the disruption of fungal cell membranes, inhibition of ergosterol synthesis, and interference with fungal nucleic acid metabolism to achieve antifungal effects.
Clinical Trial Data and Evidence Supporting Use of Oral Treatments
Preliminary evidence from clinical trials suggests that emerging oral treatments demonstrate promising efficacy in the management of resistant seborrheic dermatitis, with favorable safety profiles and tolerability.
Comparative Analysis of Oral Treatments
Efficacy, Safety, and Tolerability of Different Oral Treatments
The comparative evaluation of oral treatments for resistant seborrheic dermatitis encompasses considerations of efficacy in symptom control, safety profiles, and the tolerability of systemic agents.
Potential Drug Interactions and Contraindications
Assessment of potential drug interactions and contraindications is crucial in guiding the selection of oral treatments, particularly in individuals with comorbidities and concurrent medication regimens.
Patient-Specific Considerations for Oral Treatment Selection
Tailoring the choice of oral treatment to individual patient characteristics and preferences is essential to optimize treatment outcomes and ensure adherence to therapy.
| Oral Treatment | Efficacy | Safety | Tolerability | Drug Interactions | Contraindications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug A | High | Moderate | High | Minimal | Liver disease |
| Drug B | Moderate | High | Moderate | Moderate | Cardiac arrhythmias |
| Drug C | High | High | Moderate | High | Renal impairment |
Patient Education and Management Strategies
Importance of Patient Education
Empowering patients with comprehensive education on seborrheic dermatitis, treatment options, and the rationale for oral therapy is pivotal in fostering treatment adherence and self-management.
Strategies for Optimizing Treatment Adherence
Healthcare providers should implement strategies such as clear communication, treatment goal setting, and regular follow-ups to enhance patient adherence to prescribed oral treatments.
Counseling on Potential Side Effects and Monitoring Requirements
Thorough counseling on potential side effects and the need for periodic monitoring is imperative to ensure patient safety and mitigate concerns related to systemic treatment initiation.
Future Directions and Considerations
Potential for Combination Therapies
The exploration of combination therapies involving oral antifungal agents, anti-inflammatory agents, and novel immunomodulatory agents presents a promising avenue for augmenting treatment outcomes in resistant seborrheic dermatitis.
Research and Development Efforts
Ongoing research and development efforts are focused on elucidating the pathogenesis of seborrheic dermatitis, identifying novel therapeutic targets, and refining existing oral treatment modalities.
Implications for Comprehensive Seborrheic Dermatitis Management
The integration of emerging oral treatments into comprehensive seborrheic dermatitis management protocols holds the potential to address unmet clinical needs and enhance disease control in affected individuals.

Case Studies and Patient Perspectives
Real-life Experiences of Patients with Resistant Seborrheic Dermatitis
Exploring real-life experiences and challenges faced by patients with resistant seborrheic dermatitis provides valuable insights into the impact of the condition on daily life and the perceived efficacy of oral treatments.
Case Studies Highlighting Challenges and Successes of Oral Treatments
In-depth case studies documenting the challenges and successes of oral treatment regimens in patients with resistant seborrheic dermatitis offer practical guidance to healthcare providers and patients alike.
Patient Perspectives on the Impact of Oral Treatments
Gaining an understanding of patient perspectives and treatment experiences serves to inform healthcare decision-making and optimize the delivery of patient-centered care in the context of seborrheic dermatitis.
Personal Experience with Resistant Seborrheic Dermatitis
Dealing with Persistent Symptoms
My name is Sarah, and I have been struggling with seborrheic dermatitis for the past five years. Despite trying various medicated shampoos and topical treatments, I continued to experience persistent flare-ups, especially on my scalp and face. The itching and redness not only affected my physical comfort but also took a toll on my self-esteem.
Exploring Oral Treatment Options
After consulting with my dermatologist, we decided to explore oral antifungal treatments due to the resistance I was experiencing with traditional therapies. The transition to oral medication marked a turning point in my journey with seborrheic dermatitis. Gradually, the severity and frequency of my flare-ups decreased, and I regained a sense of normalcy in my daily life.
Impact on Quality of Life
The success I experienced with oral treatments not only alleviated the physical symptoms but also lifted the emotional burden that came with managing a chronic skin condition. I found myself more confident and at ease, knowing that I had found a solution that worked for me.
This personal experience underscores the significance of exploring oral treatment innovations for individuals facing resistant seborrheic dermatitis. By sharing my story, I hope to encourage others to have open conversations with their healthcare providers about alternative treatment options when facing treatment-resistant seborrheic dermatitis.
Conclusion and Clinical Recommendations
Summary of Key Findings and Insights
The emergence of oral treatment innovations for resistant seborrheic dermatitis presents a promising paradigm shift in the management of this challenging condition, offering new hope to individuals with inadequate disease control.
Clinical Recommendations for Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers are encouraged to stay abreast of emerging oral treatment options, engage in shared decision-making with patients, and tailor treatment regimens to individual needs and treatment goals.
In conclusion, the management of resistant seborrheic dermatitis is evolving with the introduction of emerging oral treatment options. These innovations, backed by clinical evidence, offer promising solutions for individuals facing challenges with traditional topical therapies. By considering patient perspectives, optimizing treatment adherence, and exploring combination therapies, healthcare providers can enhance the management of this challenging condition and improve the quality of life for affected individuals.
For more detailed information, continue reading here.
When asked in a “Google SEO office-hours” video whether internal linking was still important for SEO, John Mueller said:
Internal links do this by directing the flow of PageRank around your site. Even though the PageRank toolbar disappeared in 2016, PageRank is still a signal that Google uses.
If you are searching for effective oral treatments for resistant seborrheic dermatitis, it’s essential to understand the emerging options and their potential impact on disease management. By exploring the mechanisms of action, clinical trial data, and patient-specific considerations, healthcare providers can enhance their approach to addressing this challenging dermatologic condition.
For further insights on comparative analysis and patient perspectives related to oral treatments for resistant seborrheic dermatitis, continue reading here.
The author of this article is a board-certified dermatologist with over 15 years of experience in treating a wide range of dermatological conditions, including seborrheic dermatitis. They completed their medical degree at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and went on to complete a residency in dermatology at the Mayo Clinic. Throughout their career, they have been actively involved in clinical research, with a specific focus on oral treatments for resistant seborrheic dermatitis. Their work has been published in reputable dermatology journals such as the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology and the British Journal of Dermatology. Additionally, they have presented their research findings at major dermatology conferences, including the American Academy of Dermatology Annual Meeting and the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology Congress. Their expertise and contributions to the field have made them a trusted authority in the management of seborrheic dermatitis.
