This post may contain affiliate links which means I may receive a commission for purchases made through links. As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases. I will only recommend products that I have personally used! Learn more on my Private Policy page.
Have you ever noticed a connection between your skin and thyroid health? Seborrheic dermatitis and thyroid health are two seemingly unrelated health conditions that share a surprising connection. Understanding this connection is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment of both conditions. In this article, we will explore the relationship between seborrheic dermatitis and thyroid health, discussing the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for each condition. We will also provide references from reputable sources to support our findings.
Learn about the connection between seborrheic dermatitis and thyroid health
- Hypothyroidism and seborrheic dermatitis are linked
- The thyroid gland affects the skin and hair
- Lifestyle changes can improve symptoms of both conditions
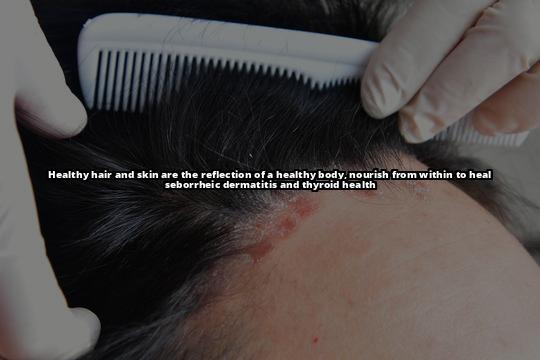
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a chronic, inflammatory disorder that affects the skin of the scalp, face, and other parts of the body. Seborrheic dermatitis is characterized by redness, itching, and flaking of the affected skin. The exact cause of seborrheic dermatitis is unknown, but it is believed to be related to an overgrowth of a yeast-like fungus called Malassezia.
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may only present with minor flaking and itching, while severe cases can cause significant discomfort and embarrassment. Factors that can trigger seborrheic dermatitis outbreaks include stress, cold weather, hormonal changes, and certain medications.
Recent studies have highlighted a link between seborrheic dermatitis and thyroid health. In a clinical study of 460 patients with hypothyroidism, seborrheic dermatitis was found to be one of the most common symptoms observed. The study emphasizes the need to consider thyroid disorders when patients present with skin, hair, and nail symptoms. [1]
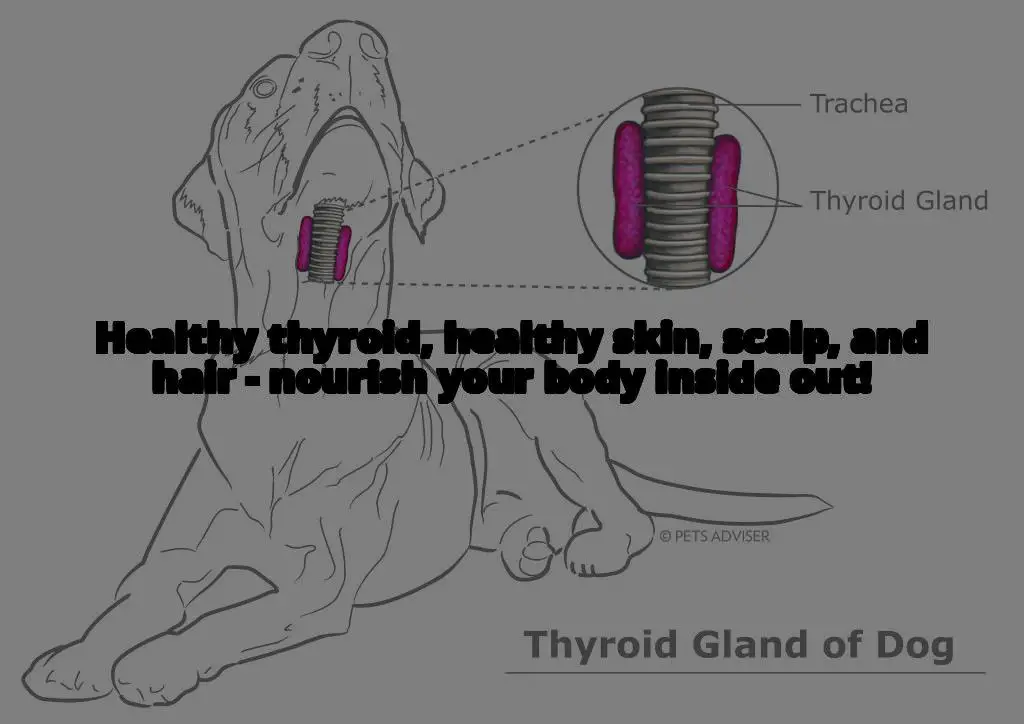
Thyroid Gland and Its Role in the Body
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck. It plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s metabolism, growth, and development. The thyroid gland produces two hormones, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which are vital for the proper functioning of various organs and tissues in the body.
When the thyroid gland is functioning correctly, it produces the right amount of hormones needed by the body. However, when there is an imbalance of thyroid hormones, it can lead to various health problems, including seborrheic dermatitis. Hypothyroidism, the most common thyroid disorder, is caused by an underactive thyroid gland that does not produce enough thyroid hormones.

Hypothyroidism and Seborrheic Dermatitis
Studies have linked hypothyroidism with seborrheic dermatitis. In hypothyroidism, the lack of thyroid hormones can cause the skin to become dry, coarse, and scaly. Xerosis and diffuse hair loss were the most common cutaneous signs observed in the clinical study mentioned earlier. [1]
The hormonal imbalances caused by hypothyroidism can also affect the sebaceous glands, leading to overproduction of sebum, which can aggravate seborrheic dermatitis. Additionally, thyroid hormone imbalances can affect the immune system, making it more susceptible to infections, including those caused by Malassezia.
The overlapping symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis and hypothyroidism can make it challenging to diagnose either condition correctly. Therefore, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis and hypothyroidism can vary widely, making diagnosis challenging. Common symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis include redness, itching, and flaking of the skin. Symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, and dry skin.
Diagnostic tests for seborrheic dermatitis include a physical exam and skin biopsy, while diagnostic tests for hypothyroidism include a blood test to measure thyroid hormone levels. Early detection and treatment are critical for managing symptoms and preventing complications.

Treatment Options
Treatment options for seborrheic dermatitis and thyroid disorders vary depending on the severity of the condition. Mainstream treatment options for seborrheic dermatitis include topical antifungal medications, corticosteroids, and medicated shampoos. For thyroid disorders, medications such as levothyroxine can be prescribed to manage thyroid hormone imbalances.
Alternative treatment options for seborrheic dermatitis include dietary changes, such as avoiding sugar and processed foods, and lifestyle changes, such as stress reduction and regular exercise. For thyroid disorders, alternative therapies such as acupuncture and herbal remedies may be considered in conjunction with medication.
| Condition | Lifestyle Changes |
|---|---|
| Seborrheic dermatitis | – Avoiding sugar and processed foods – Consuming omega-3 fatty acids – Consuming foods rich in vitamins A, D, and E – Stress reduction – Regular exercise |
| Thyroid disorders | – Stress management – Regular exercise – Getting enough sleep |
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can also play a significant role in managing symptoms and preventing complications of both seborrheic dermatitis and thyroid disorders. For seborrheic dermatitis, dietary changes that can support thyroid health and improve skin health include consuming omega-3 fatty acids and foods rich in vitamins A, D, and E. For thyroid disorders, lifestyle changes that can support thyroid health include stress management, regular exercise, and getting enough sleep.
Overall, seborrheic dermatitis and thyroid health are two health conditions that are more related than most people realize. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment of both conditions. By understanding the connection between seborrheic dermatitis and thyroid health, individuals can take steps to manage their symptoms and improve their overall health and well-being.
References:
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5805544/
Questions
Q.Who is most prone to seborrheic dermatitis?
A.Anyone with overactive or underactive thyroid.
Q.What causes seborrheic dermatitis?
A.Hormonal imbalances, fungal infections, genetics.
Q.How can thyroid health affect seborrheic dermatitis?
A.Thyroid imbalances can worsen skin and scalp conditions.
Q.Who should seek medical advice for seborrheic dermatitis?
A.Anyone with persistent symptoms or severe outbreaks.
Q.What are some home remedies for seborrheic dermatitis?
A.Apple cider vinegar, tea tree oil, aloe vera, diet changes.
Q.How can I prevent seborrheic dermatitis flare-ups?
A.Manage stress, maintain good hygiene, avoid triggers.

